If the traditional sewage treatment mode is used for industrial sewage treatment, it is still a large energy consumer. Because traditional wastewater treatment requires a large amount of fuel and chemicals, it indirectly emits a large amount of greenhouse gases, and the treatment process itself will also directly emit greenhouse gases. So in essence, traditional sewage treatment is energy consumption in exchange for water quality. Therefore, in order to reduce carbon emissions, reducing energy and material consumption for sewage treatment is an inevitable goal for industry upgrading.
For example, zero discharge of industrial wastewater from coal-fired power plants can be achieved in the reuse technology of "pretreatment (softening + coagulation + clarification) + deep desalination (membrane filtration/electrodialysis)", "acid-base adjustment + flocculation and precipitation + filtration and clarification" reuse technology, "physicochemical oil separation + air flotation separation + filtration/adsorption" technology, "pretreatment + concentration and reduction + crystallization and solidification" and other methods to achieve the purpose of zero discharge and realize the recycling of wastewater.
For example, there is zero discharge of high-salt wastewater in chemical plants, and the evaporation crystallization treatment process commonly used in the industry can complete the resource utilization of wastewater through steps such as pretreatment, heat exchange, crystalline solid and liquid separation, liquid recycling and recovery, and distilled water reuse. Among them, falling film mechanical vapor recompression circulation evaporation, mechanical vapor recompression evaporation, thermal vapor recompression evaporation, multi-effect evaporation and other methods have their own merits.
It can also be seen that a common path for the green development of industrial wastewater treatment is to realize recycling, including the recycling of energy and organic matter, which is more typical of the mature application of foreign phosphorus recycling technology in sewage.
On the other hand, the development of membrane technology will also greatly promote the process of industrial wastewater treatment towards "zero discharge". In addition to the zero discharge of membrane industrial sewage treatment, it is also very necessary to actively take various measures to achieve energy reduction according to local conditions.
Process Description:
The conventional process flow of the zero-emission process treatment system mainly includes pretreatment process, membrane treatment process, evaporation crystallization process and auxiliary process.
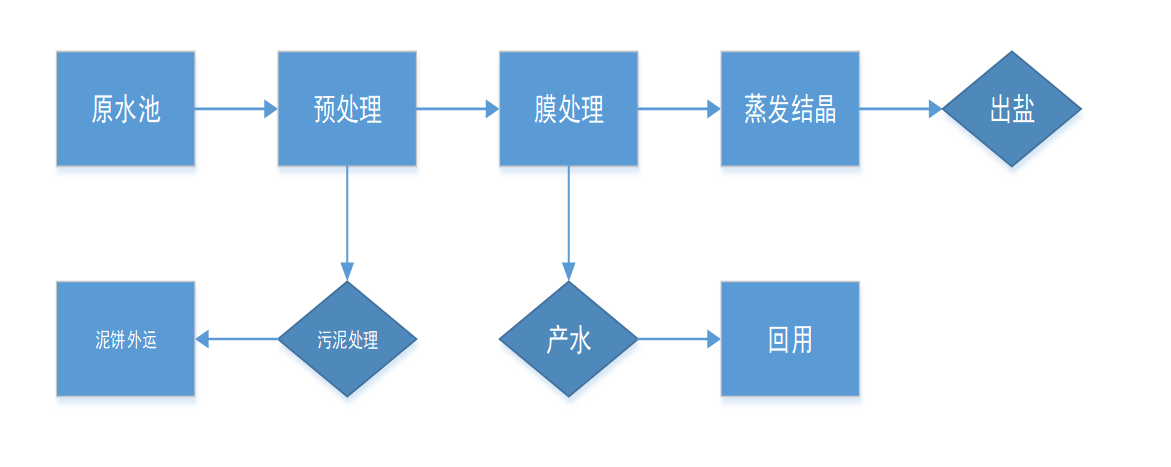
The raw water enters the raw water tank to stabilize the water quality and quantity, and the suspended or colloidal impurities in the water are removed through the lifting of the lifting pump and the filtration of the multi-media filter, and the effluent of the multi-media filter further removes the suspended solids in the wastewater through the security filter, with a filtration accuracy of 10μm, providing the last protective barrier for the OCRO membrane. In order to prevent the fouling of various insoluble sulfates and silicates in the membrane module due to high concentration, and effectively prolong the service life of the membrane, a certain amount of scale inhibitor needs to be added before entering the OCRO. The amount of addition is determined by the concentration of insoluble salts in the raw water. The wastewater passing through the cartridge filter is directly boosted by an OCRO-W high-pressure pump and enters the first-stage OCRO-W system for treatment, and the first-stage OCRO-W demineralized water enters the production tank.
The first-stage OCRO-W brine enters the first-stage OCRO-L system through the action of the concentrated water booster pump and the pressure boost of the high-pressure pump, and the produced water of the OCRO-L system is mixed with the produced water of the first-stage OCRO-W system into the production tank, and the concentrated water enters the MVR evaporation crystallization system, and finally the salt is produced to achieve the purpose of zero discharge.


